Automated artifact rejection
Load the sample EEGLAB dataset
Select menu item File and press sub-menu item Load existing dataset. Select the tutorial file “eeglab_data.set” distributed in the “sample_data” folder of EEGLAB. Then press Open.
Automated artifact rejection with Clean Rawdata plugin
Clean_rawdata is an EEGLAB plugin installed by default with EEGLAB. It can remove both bad data channels and bad portions of data. Select menu item Tools and press sub-menu item Reject data using Clean Rawdata and ASR.

There are several sections to this menu indicating different sequential processes:
-
The top section is about high-pass filtering your data. By default, this option is not selected since EEGLAB assumes that you might have already filtered your data. However, if this is not the case, you may select that option. The frequency limits indicate the transition bandwidth for the high pass filter (so 0.25 to 0.75 Hz indicate a high-pass filter at 0.5 Hz).
-
The second option deals with removing bad channels. There are three methods to remove bad channels. Flat channels may be removed. Channels with a large amount of noise may be removed based on their standard deviation, and channels, which are poorly correlated with other channels, may be removed. The rejection threshold for channel correlation is set to 0.8. Note that channel rejection based on their correlation is performed differently if you have imported channel locations (a different heuristic that takes into account channel location is used in case you have them - and we strongly advise importing channel locations before automated artifact rejection).
-
The third section deals with rejecting bad portions of data using the Artifact Subspace Reconstruction (ASR) algorithm. The full description of this algorithm is outside the scope of this tutorial. For more information, we refer to this Appendix. ASR may be used to correct bad portions of data or to remove them. For offline EEG processing, we advise to remove them, which corresponds to the default options. First, ASR finds clean portions of data (calibration data) and calculates PCA-extracted components’ standard deviation (ignoring physiological EEG alpha and theta waves by filtering them out). It rejects data regions if they exceed 20 times (by default) the standard deviation of the calibration data. The lower this threshold, the more aggressive the rejection is. The Riemannian distance is an experimental metric published in this article that claims superior performance – ASR’s author C. Kothe disputes its claims.
-
The fourth option deals with the additional rejection of bad portions of data based on a set number of channels passing a standard deviation threshold in a given time window. The time window size can be fine-tuned when running the function from the command line. This allows rejecting bad portions of data that ASR might have missed.
-
The last option allows plotting results of the rejection with rejected data highlighted.
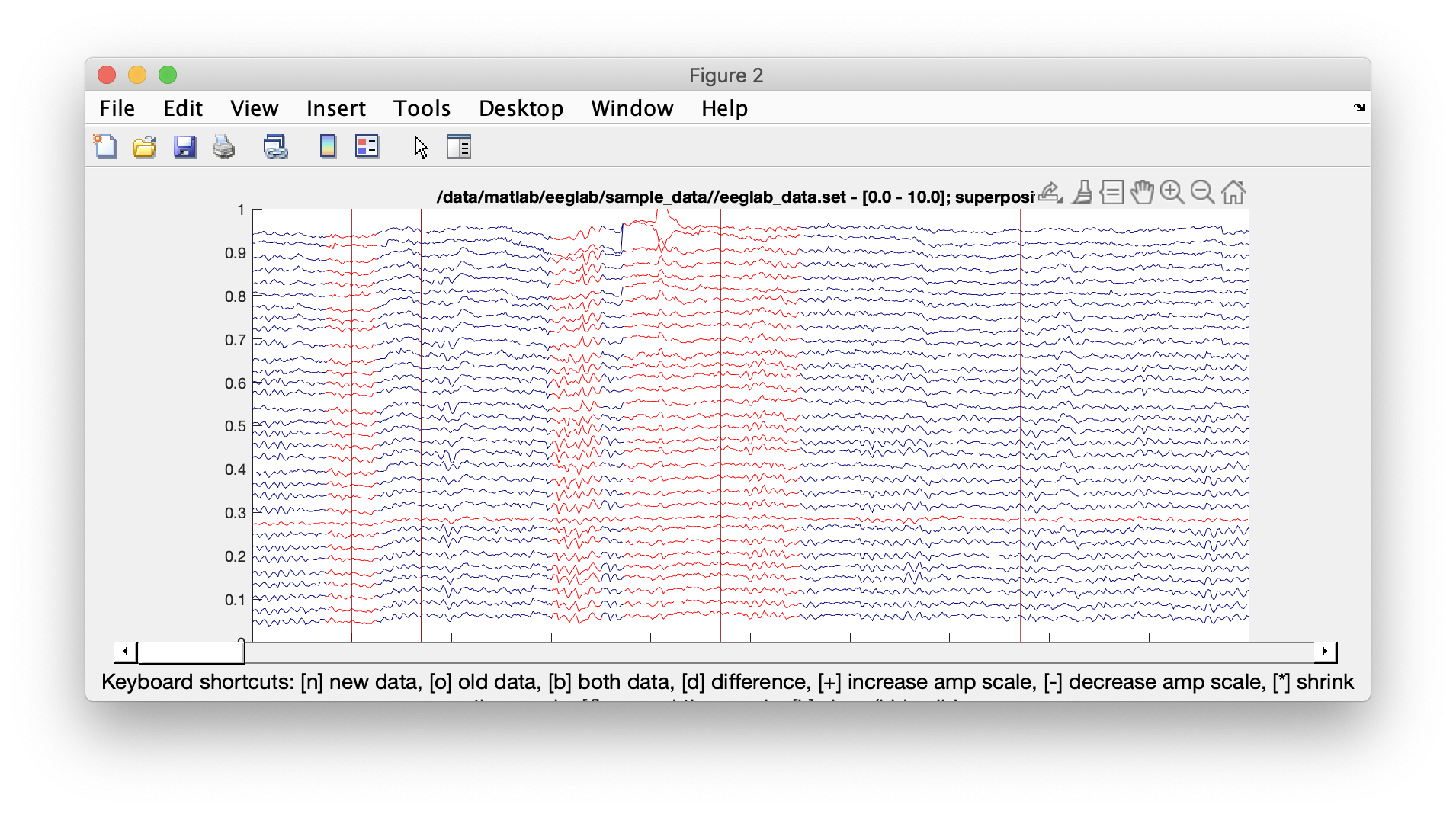
The result of rejecting data on the tutorial dataset are shown below. We can see the rejected channels in red and the rejected data portion when all channels are marked in red in a given time segment. If correcting data using the ASR algorithm (not shown here), the old and new (corrected) data will be overlaid. We do not recommend using ASR correction (as opposed to rejection) on pre-recorded data because this functionality was primarily developed for real-time applications. The consequences of using ASR on EEG post-processing are not clearly understood – although an increasing number of articles are being published on this subject.
Automated artifact rejection using other methods
The are several EEGLAB plugins and legacy EEGLAB menus to reject bad data and bad channels. Use menu item File → Preference and check the checkbox to If set, show all menu items from previous EEGLAB versions. Restart EEGLAB for this change to take effect. A collection of menu items for rejecting bad portions of data become available. These involve Tools → Automatic channel rejection (see the help message of the pop_rejchan.m function) and Tools → Automatic continuous rejection (see help of the pop_rejcont.m function), which were the default methods used in previous versions of EEGLAB. A collection of menus to reject bad data epochs is also described in this section of the tutorial.