Data for the tutorial
This tutorial aims at teaching how to use LIMO MEEG, in conjunction with EEGLAB STUDY. To get started, you must be familiar with EEGLAB. Also, make sure LIMO tools subdirectories are listed in the Matlab path.
The data used in this tutorial come from Wakeman and Henson (2015). In this experiment, MEG-EEG data were collected while subjects viewed famous, unfamiliar and scrambled faces. Each image was repeated twice (immediately in 50% of cases and 5–10 stimuli apart for the other 50%) and subjects pressed one of two keys with their left or right index finger indicating how symmetric they regarded each image relative to the average.
The data were prepared (i.e. EEG extracted, timing corrected, electrode position re-oriented, event recorded) by Dung Truong, Ramon Martinez & Arnaud Delorme and can be downloaded from OpenNeuro.
Data pre-processing pipeline script
The data are organized according to the Brain Imaging Data Structure, in particular the EEG BIDS extension. It is worthwhile spending a bit of time looking at how files are organized and named, as we will follow this convention throughout. EEGLAB also has dedicated BIDS tools called bids-matlab-tools to create files, export and import BIDS dataset. This is available using the EEGLAB plugin manager and must be installed before running the code below.
Once you have downloaded the data, you can run the code below - can copy and paste to a file (changing Xs with your specific path) to get descent pre-processed data. Alternatively download the code located here. Be patient, this step will take several hours.
% start EEGLAB
clear variables
[ALLEEG, EEG, CURRENTSET, ALLCOM] = eeglab;
% import BIDS
bidsfolder = 'F:\WakemanHenson_Faces\eeg';
[STUDY, ALLEEG] = pop_importbids(bidsfolder, 'bidsevent','on','bidschanloc','on', ...
'eventtype', 'trial_type', 'outputdir' ,fullfile(bidsfolder,'newderivatives'), 'studyName','Face_detection');
ALLEEG = pop_select( ALLEEG, 'nochannel',{'061','062','063','064'});
CURRENTSTUDY = 1; EEG = ALLEEG; CURRENTSET = 1:length(EEG);
% reorient if using previous version of the data
EEG = pop_chanedit(EEG,'nosedir','+Y');
% Clean data - just the bad channels
EEG = pop_clean_rawdata( EEG,'FlatlineCriterion',5,'ChannelCriterion',0.8,...
'LineNoiseCriterion',4,'Highpass',[0.25 0.75] ,...
'BurstCriterion','off','WindowCriterion','off','BurstRejection','off',...
'Distance','Euclidian','WindowCriterionTolerances','off' );
% Rereference using average reference
EEG = pop_reref( EEG,[],'interpchan',[]);
% Run ICA and flag artifactual components using IClabel
for s=1:size(EEG,2)
EEG(s) = pop_runica(EEG(s), 'icatype','runica','concatcond','on','options',{'pca',EEG(s).nbchan-1});
EEG(s) = pop_iclabel(EEG(s),'default');
EEG(s) = pop_icflag(EEG(s),[NaN NaN;0.8 1;0.8 1;NaN NaN;NaN NaN;NaN NaN;NaN NaN]);
EEG(s) = pop_subcomp(EEG(s), find(EEG(s).reject.gcompreject), 0);
end
% clear data using ASR - just the bad epochs
EEG = pop_clean_rawdata( EEG,'FlatlineCriterion','off','ChannelCriterion','off',...
'LineNoiseCriterion','off','Highpass','off','BurstCriterion',20,...
'WindowCriterion',0.25,'BurstRejection','on','Distance','Euclidian',...
'WindowCriterionTolerances',[-Inf 7] );
% Extract data epochs (no baseline removed)
EEG = pop_epoch( EEG,{'famous_new','famous_second_early','famous_second_late','scrambled_new','scrambled_second_early','scrambled_second_late','unfamiliar_new','unfamiliar_second_early','unfamiliar_second_late'},...
[-0.5 1] ,'epochinfo','yes');
EEG = eeg_checkset(EEG);
EEG = pop_saveset(EEG, 'savemode', 'resave');
ALLEEG = EEG;
% Create study design
STUDY = std_checkset(STUDY, ALLEEG);
STUDY = std_makedesign(STUDY, EEG, 1, 'name','STUDY.FaceRepetition','delfiles','off','defaultdesign','off','variable1','type','values1',{});
eeglab redraw
Loading the pre-processed EEGLAB STUDY
After data preprocessing, data should be clean, epochs marked, and a STUDY created. Load the study from the EEGLAB menu (File –> Load existing study - figure 1) and check that all the data are there (Study –> edit study info - figure 2). In total there are 18 subjects, named sub-002 to sub-019.
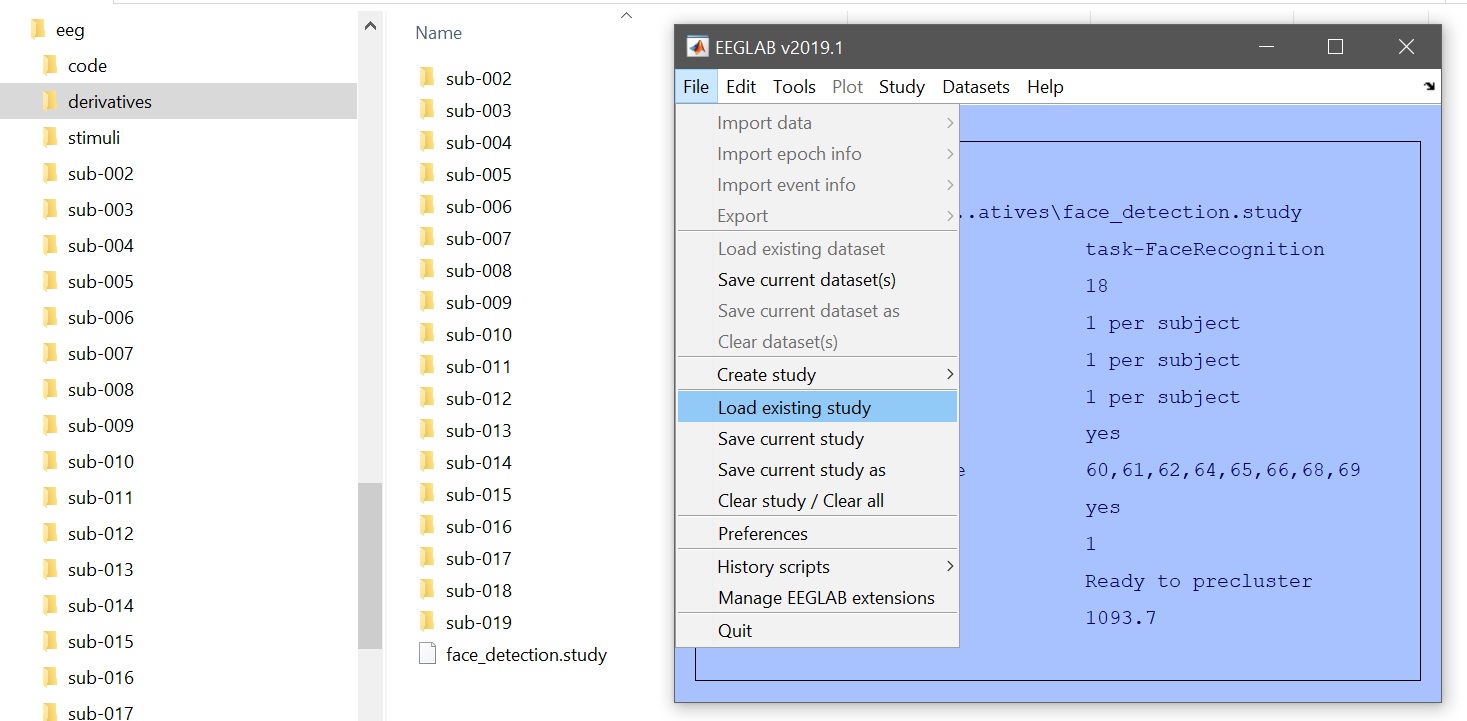 Figure 1. Loading EEGLAB STUDY
Figure 1. Loading EEGLAB STUDY
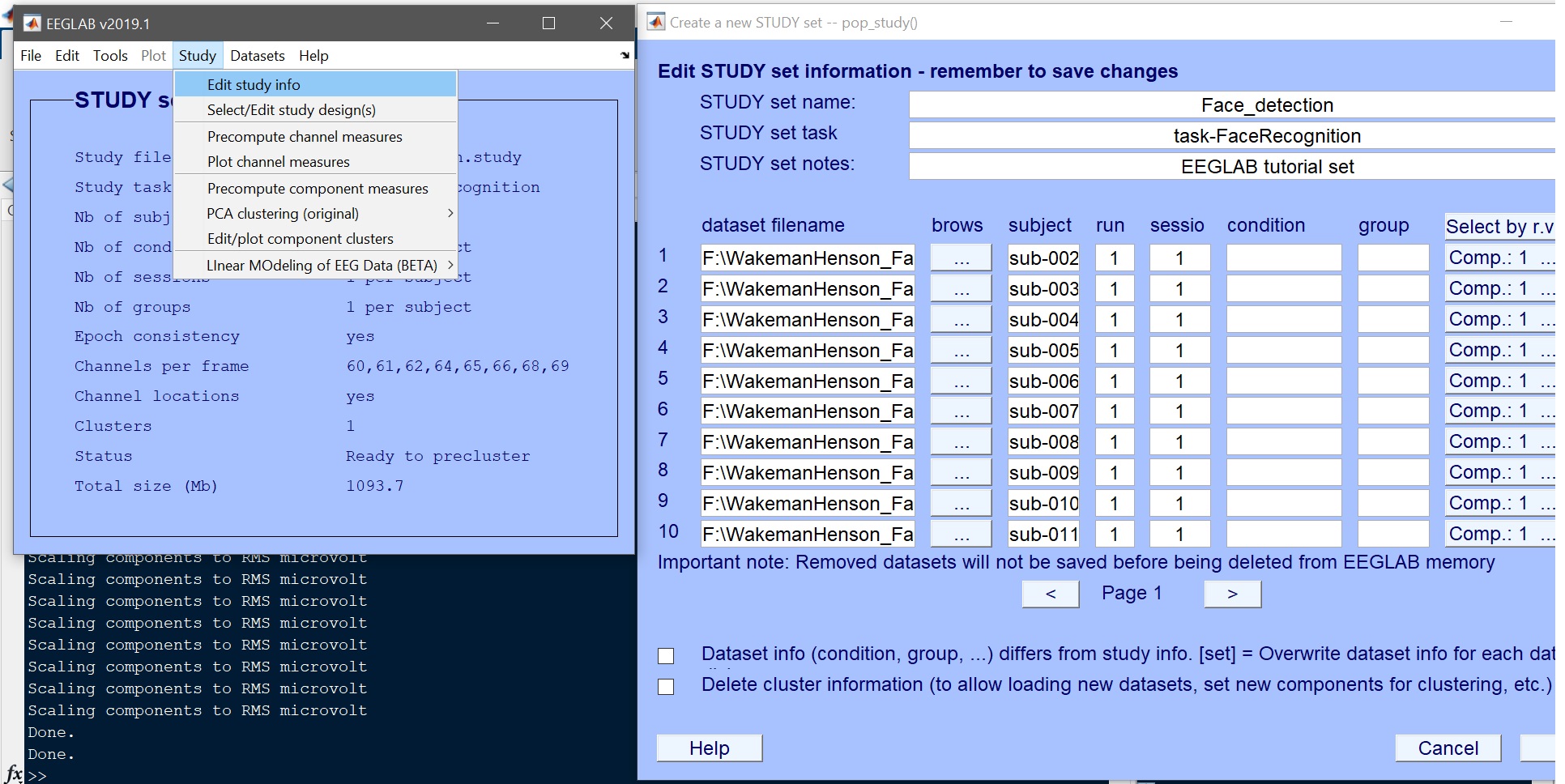 Figure 2. Wakeman_Henson STUDY
Figure 2. Wakeman_Henson STUDY
Precompute STUDY measures
LIMO MEEG models data using a hierarchical approach with a general linear model at the subject level and then testing, at the group level, parameters obtained with robust methods. You can think of it as generating averages per condition at the subject level and do statistics on those averages at the group level. The difference (and advantage) is that subject-specific baselines are removed, among trial variance accounted for, and bad subjects are accounted for. For more details see the San Diego 2016 lecture as pdf and/or on YouTube.
Step 1 – precompute single-trial measure(s)
No matter the design, using LIMO MEEG means we need single trials to obtain condition related parameters for each subject. EEGLAB will export all trial data measures and, depending on the design, will pass on only relevant ones to LIMO EEG (even if this is only the mean as for comparing spectra between groups).
Create ERPs and/or Spectra and/or ERSP (Study –> Precompute channel measures – figure 3). Note you could set limits to your epoch at this stage (using ‘timelim’ and ‘freqlim’) or limit the statistical analysis at the next stage (which is what we will do). For ERPs, baseline correction can be added using [-200 0]. Note that ERSP can take a long time. You can start with ERP and Spectra only (of course if you do that, you will not be able to use LIMO on ERSP in the next sections).
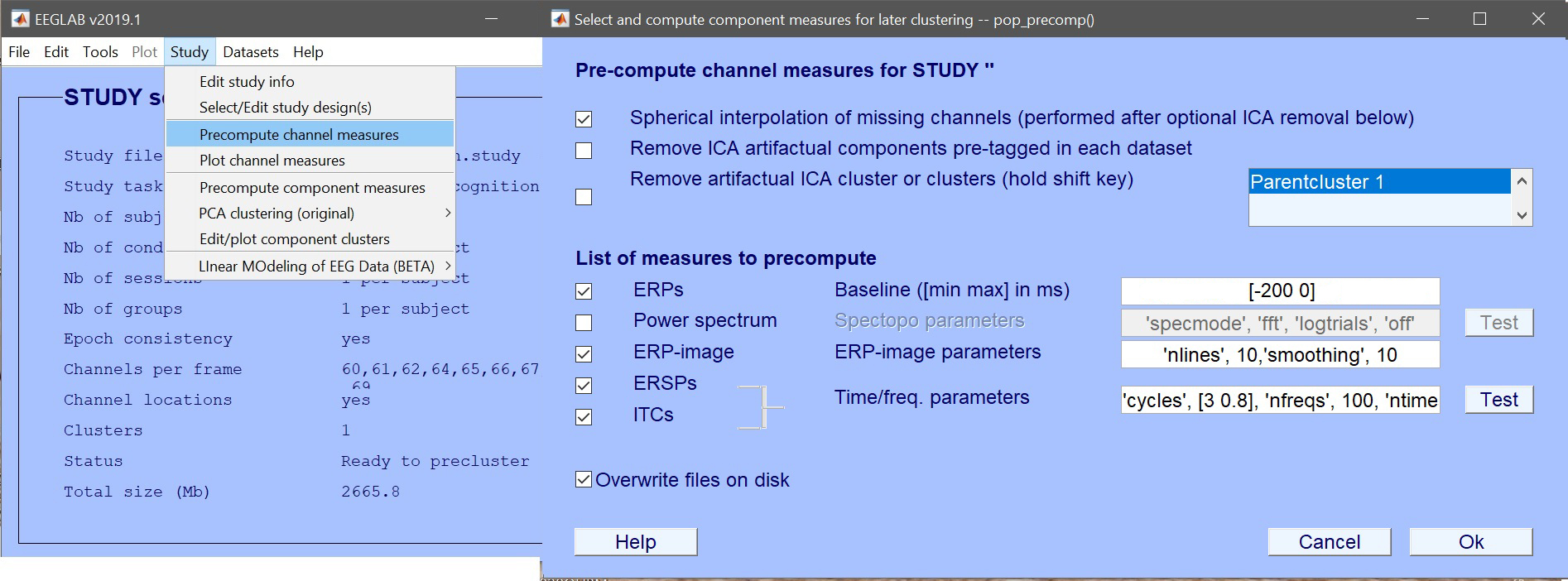
Figure 3. Precompute channel measures
All single trials (erp, spectrum, ersp) can also be generated in command line using:
% Precompute ERP and Spectrum measures
[STUDY, EEG] = std_precomp(STUDY, EEG, {}, 'savetrials','on','interp','on','recompute','on',...
'erp','on','erpparams', {'rmbase' [-200 0]}, 'spec','on',...
'ersp','on','itc','on', 'specparams',{'specmode','fft','logtrials','off'});
Step 2 – create your design
From a set of available conditions and trial information, there are many options available. In this tutorial, we’ll review the most common ones. For example, we can select the independent variable “face_type” that takes 3 categorical values (famous, scambled and unfamiliar faces). We will start by using this simple design and create more complex ones as we go along the tutorial (Study –> Select/Edit study designs(s) – figure 4).
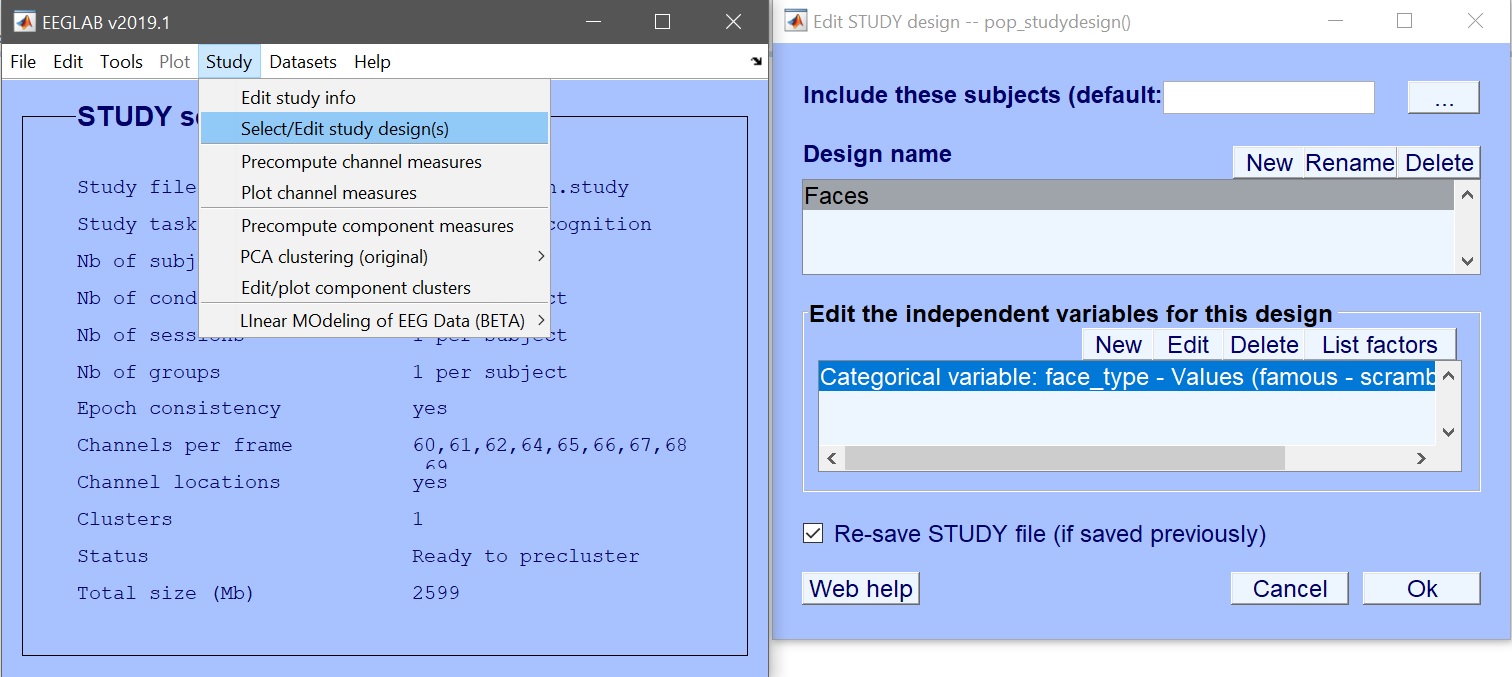 Figure 4. Select/Edit study design(s)
Figure 4. Select/Edit study design(s)
Every design can be generated from here, and the following sections will show you each time a different design. For now, let’s have a look at the ‘List of factors’ (figure 5). This lists all categorical variables from which we can make a design (this list appears if you select “list factors” for the independent variable). This list of factors is the list LIMO will use at the first level. In the next section, we will do a 1-way ANOVA testing the effect of familiarity (all famous vs. all unfamiliar vs. all scrambled faces).
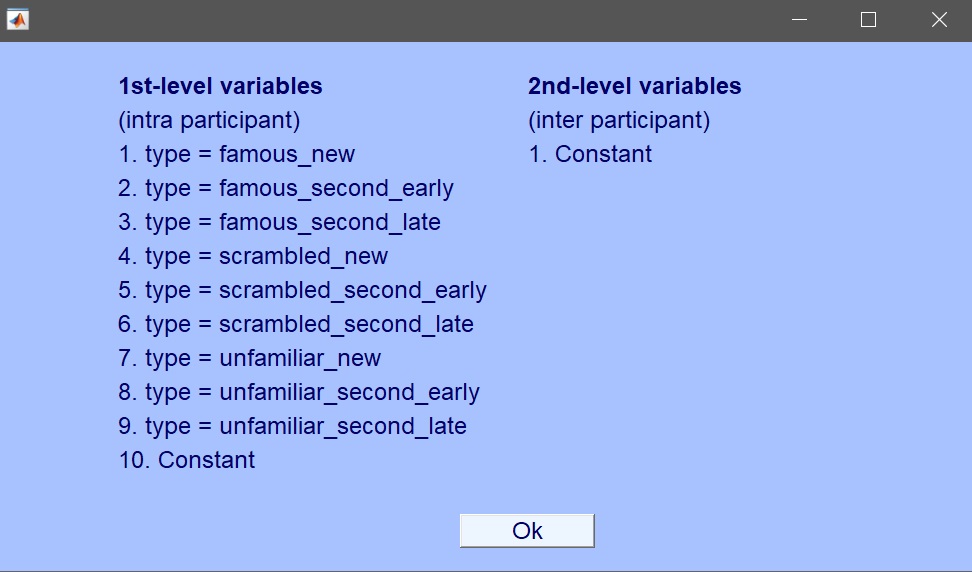 Figure 5. List of categorical variables
Figure 5. List of categorical variables
Note on using LIMO default and sampling rate
By default, LIMO EEG uses a Weighted least Squares approach for each trial, which means you should aim to have more trials than time frames (for ERP and ERSP) or frequency frames (for Spectrum), while not mandatory. The data here are at 250Hz which is fine.